Composr Tutorial: Manually editing your database with phpMyAdmin
If something goes wrong with Composr/MySQL/the-server that leaves your database in a corrupted/intermediate state, you may need to manually edit the database contents to resolve the problem. Note that it is very rare for this to occur, as Composr is designed to be fault tolerant in common situations, but it can never fully protect against all situations such as those that might be triggered by a power-cut at a critical time, or a faulty disk.
phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin as found in the Plesk webhosting control panel
phpMyAdmin is powerful web application for managing databases and database contents.
It is also possible to install phpMyAdmin manually on almost any PHP webhosting package.
Corrupted databases
Repairing tables
- Incorrect key file for table
- Can't write; duplicate key in table
- Table was marked as crashed and should be repaired
- (…) is marked as crashed and last automatic repair failed
Composr does provide an interface to the repair mechanism in the upgrader.php script, but if corruption is very bad, you may not be able to reach it. In this case, you will need to use phpMyAdmin, as shown in the screen-shot.
Note that if it looks like corruption has happened due to a physical disk problem, then it is absolutely crucial you back up Composr (and anything else on the server) as soon as humanely possible and make sure the server gets a disk scan, and if necessary, a new hard disk. Disk issues tend to spread, and files that touch the damaged area are 'scarred': an initially small problem could quickly irreparably destroy all your data.
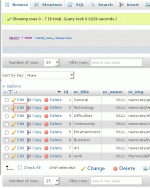
Browsing the database
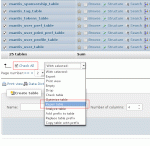
Choosing a table to edit rows of
Choosing a row to edit
Editing a row
- tables
- rows
- fields
A table is basically defined by a name, and the fields it contains. That table then contains many rows that specify data for each of the table fields. Databases have a special concept of a row field-value being NULL; a NULL value might indicate many things, such as:
- an unknown value
- a non-calculated value
- N/A
All tables have a 'key' that allows the unique identification of any row without having to know the whole contents of that row. Usually keys are just unique numbers (IDs) assigned to rows automatically. Some people advocate choosing keys from data, but this presents problems if the data that makes up the key needs to change; for example, a username could be used as a key to a member table, but if the username was changed, Composr would need to change potentially 1000s of references.
Finding IDs
To find the ID for some Composr content, the best way is to log in as someone with Admin Zone access, go to the content, and look at the page-link in the footer. You will see something like zone:page:type:id, or zone:page:id=id, or for Comcode pages zone:page (the ID is actually the whole thing).
By convention, when IDs like this are being used as keys, they are almost always given the field name id in the database. There are a few exceptions; for Comcode pages, the ID is composed of both the the_zone and the the_page database fields, and respectively, you need to take the zone and the page from the page-link.
phpMyAdmin supports very user friendly features to browse the database tables, and to make changes. To browse a table, click the table icon to the left of the table names in the left hand frame, you can then browse and sort the table contents, and select rows for modification.
Running queries
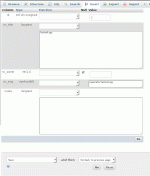
Choosing to execute an SQL query
Typing in the SQL query to execute
To run a query, you need to click the 'SQL' tab once you have chosen a database to view/edit. You then type in the query. In phpMyAdmin, it is often easier to use the interface to make changes, rather than working out what query to type. Occasionally the developers might suggest a query that could help solve a problem, as it is easier for us to give the query, than to explain all the mouse-clicks required. The screen-shots shown an example for executing a query to delete an item of news.
For a good introduction to SQL, consider reading this W3Schools SQL tutorial. These are the most basic SQL queries:
Code (SQL)
Code (SQL)
Code (SQL)
Code (SQL)
Composr database structure
This is an advanced section designed for programmers, and you may wish to skip it.At the time of writing, Composr uses 283 tables when all bundled addons are installed.
For the technically inclined, the database table structure is mostly in 4NF form, with the main exception being fields that are for caching purposes (such as post count) and other fields that remove the need for complex and slow 'JOIN's or 'EXIST's clauses.
Composr is designed to support content translatable into multiple languages, although this is off by default. If enabled, then text is located in the translate table, and linked into other places by language ID. The translate table is also used to store parsed Comcode, which works out as a very clean solution. If an entry in the translate table is being edited by hand, and has Comcode, then setting the text_parsed field to blank will cause the Comcode to be re-parsed on demand.
Composr has been designed to be able to work with many different databases, not just MySQL. We dropped official support for this feature, because like multiple language content, we could not thoroughly beta test it, especially due to very strange and varying limitations and differences in different database systems. However, Composr still avoids using MySQL-specific features wherever possible. Instead of using highly specialist (if they exist at all) queries to analyse database table structure, for systems such as backup or Conversr-member-id-migration, Composr actually stores database structure in the db_meta table. Composr's own installation techniques for creating and changing database tables will properly update this table, and if modifications are being made, it is preferable that the db_meta table is updated to reflect them.
Concepts
- Database
- Simply a system that stores structured information
- Relational database
- A system that stores information in a very strict pre-determined structure based on set-theory
- SQL
- A language for communicating with a database
- MySQL
- A free database system; Composr requires this
- phpMyAdmin
- An excellent web front-end to MySQL
- Query
- An instruction or request to a database
- Schema
- The specification of the fields rows in a table use
- Table
- A collection of rows and the schema the rows fit
- Field
- An element of a row that may store a value, of a certain type
- Row
- A number of elements that together represent a single entry of some sort
- Key
- An identifier for a row, consisting of some pre-chosen (in the schema) combination of fields
- ID
- In Composr this is a numeric identifier associated with a row, and usually also associated with a specific piece of Composr content
See also
Feedback
Have a suggestion? Report an issue on the tracker.